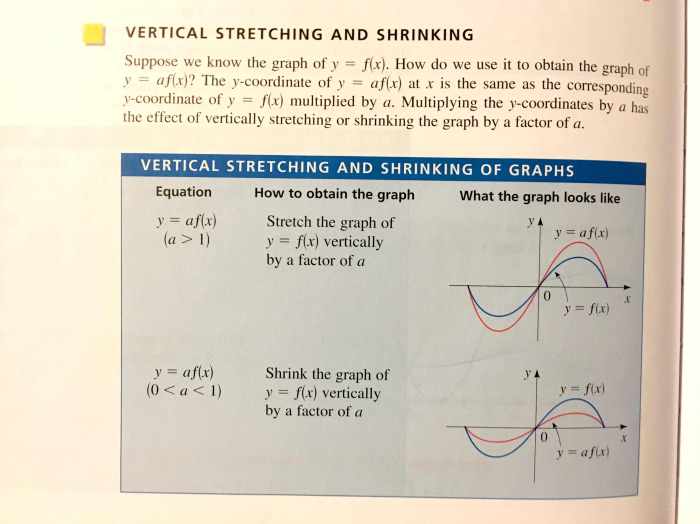
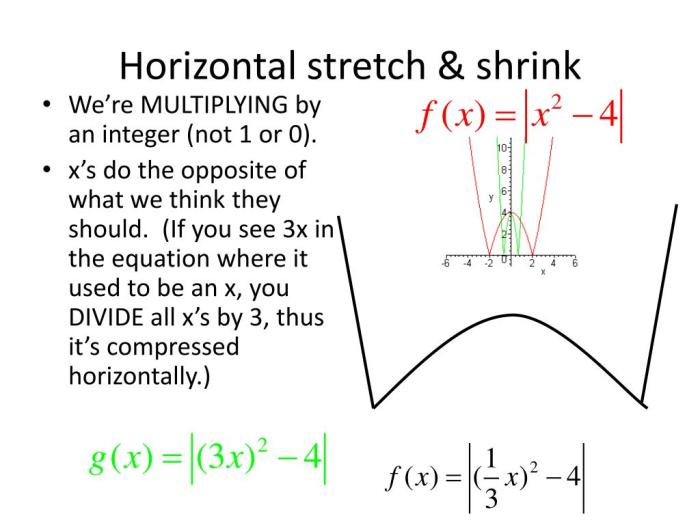
Vertical shrink by a factor of 1/3 – Vertical shrinkage by a factor of 1/3 is a fascinating concept with practical applications in various fields. This article explores the definition, applications, methods, and examples of vertical shrinkage, providing valuable insights into its significance.
The concept of vertical shrinkage involves reducing the height of an object by a factor of 1/3, often represented by mathematical equations or formulas. It has a significant impact on object dimensions, making it useful in manufacturing and design.
Vertical Shrinkage by a Factor of 1/3
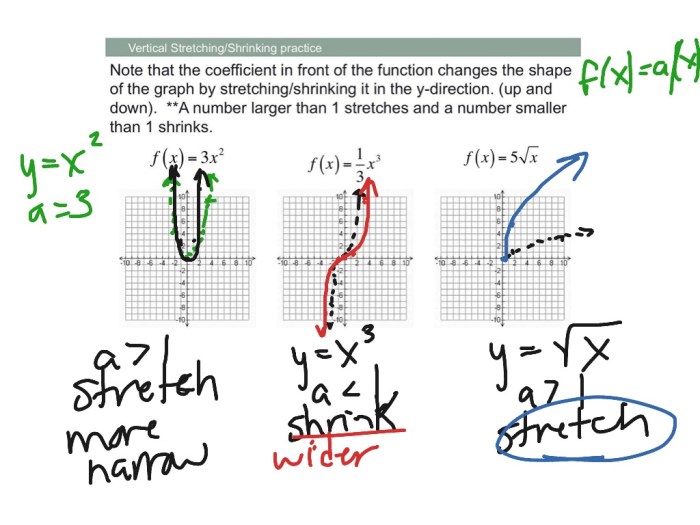
Vertical shrinkage is a technique used to reduce the height of an object by a specific factor, typically by a factor of 1/3. This reduction in height is achieved through various methods, including mechanical compression, heat treatment, or chemical processes.
Vertical Shrinkage Definition
Vertical shrinkage by a factor of 1/3 refers to the reduction in height of an object to one-third of its original height. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
$$ h_new = \frac13 h_original $$
where:
- $h_new$ is the new height after shrinkage
- $h_original$ is the original height before shrinkage
Vertical shrinkage can significantly alter the dimensions and proportions of an object, making it shorter in height while maintaining its other dimensions.
Applications of Vertical Shrinkage
Vertical shrinkage has various applications in industries such as manufacturing, design, and construction:
- Manufacturing:Vertical shrinkage can be used to reduce the size of components or products for easier handling, storage, or transportation.
- Design:Architects and designers use vertical shrinkage to create unique and visually appealing structures or objects.
- Construction:Vertical shrinkage can be employed to reduce the height of buildings or other structures, making them more suitable for certain locations or requirements.
Methods to Achieve Vertical Shrinkage
Several methods can be used to achieve vertical shrinkage by a factor of 1/3:
- Mechanical Compression:Applying pressure to the object can physically reduce its height.
- Heat Treatment:Heating the object can cause it to contract and shrink.
- Chemical Processes:Certain chemicals can react with the object’s material, causing it to shrink.
The choice of method depends on the material properties, desired shrinkage factor, and other factors.
Examples of Vertical Shrinkage, Vertical shrink by a factor of 1/3
Vertical shrinkage is used in various applications, including:
- Shrink-wrapped packaging:Plastic wrap is shrunk to tightly fit around products.
- Automotive parts:Metal components are shrunk to reduce their size and weight.
- Architectural structures:Buildings can be designed with vertical shrinkage to create unique and eye-catching designs.
Essential FAQs: Vertical Shrink By A Factor Of 1/3
What is vertical shrinkage by a factor of 1/3?
Vertical shrinkage by a factor of 1/3 refers to reducing the height of an object by one-third of its original dimension.
How is vertical shrinkage achieved?
Vertical shrinkage can be achieved through various methods, such as heat treatment, mechanical deformation, or chemical processes.
What are the advantages of using vertical shrinkage?
Vertical shrinkage offers advantages such as reduced material consumption, improved structural integrity, and enhanced dimensional accuracy.