Ocean acidification lab answer key – Delving into the realm of ocean acidification, this comprehensive lab answer key unlocks a deeper understanding of the critical issue facing our marine environments. With a focus on scientific rigor and practical experimentation, this guide provides invaluable insights into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions to ocean acidification.
Through hands-on experiments, students embark on a journey of discovery, analyzing the physiological and ecological responses of marine organisms to changing ocean conditions. The lab results offer a tangible demonstration of the profound effects of ocean acidification on marine life, highlighting the urgency of addressing this environmental challenge.
Ocean Acidification: An Overview
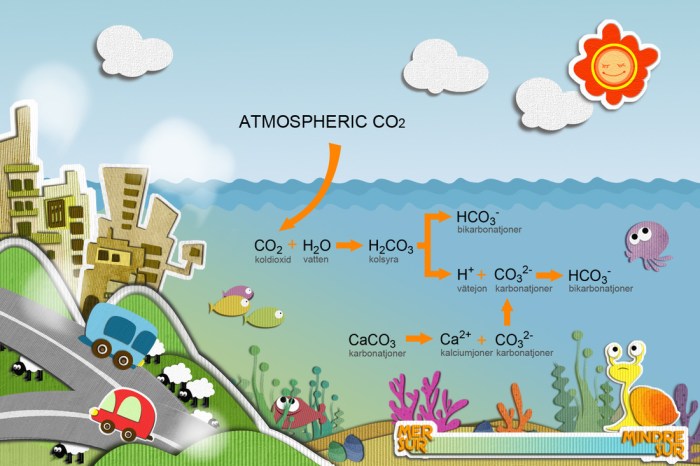
Ocean acidification refers to the ongoing decrease in the pH of the Earth’s oceans, primarily caused by the absorption of carbon dioxide (CO 2) from the atmosphere.
The process begins when CO 2dissolves in seawater, forming carbonic acid (H 2CO 3). This acid then dissociates into hydrogen ions (H +) and bicarbonate ions (HCO 3–), leading to a decrease in pH and an increase in acidity.
Causes of Ocean Acidification, Ocean acidification lab answer key
- Burning of Fossil Fuels:The combustion of fossil fuels releases large amounts of CO 2into the atmosphere, which is subsequently absorbed by the oceans.
- Deforestation:Trees and other plants absorb CO 2during photosynthesis. Deforestation reduces the Earth’s capacity to absorb CO 2, leading to increased levels in the atmosphere and oceans.
- Industrial Processes:Certain industrial activities, such as cement production and chemical manufacturing, also release significant amounts of CO 2.
Effects of Ocean Acidification on Marine Life
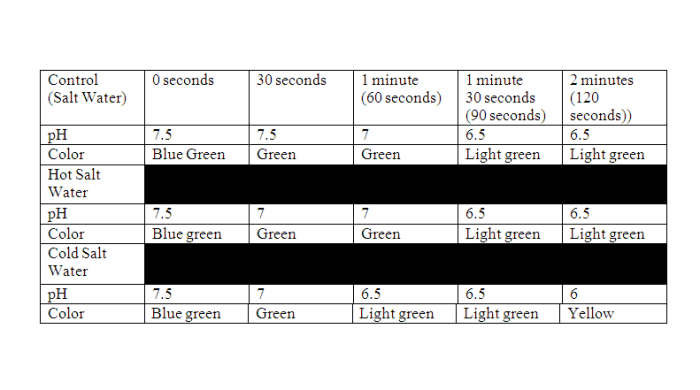
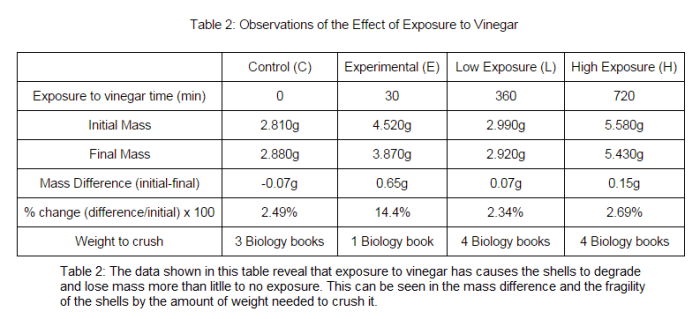
Ocean acidification has severe consequences for marine organisms, particularly those with calcium carbonate shells or skeletons.
- Reduced Shell and Skeleton Formation:Lower pH levels make it more difficult for organisms like corals, shellfish, and certain types of plankton to build and maintain their protective structures.
- Impaired Growth and Reproduction:Acidified waters can interfere with the growth and reproductive success of many marine species.
- Altered Behavior:Ocean acidification has been linked to changes in the behavior of some marine organisms, including reduced predator avoidance and increased vulnerability to predators.
Commonly Asked Questions: Ocean Acidification Lab Answer Key
What is the primary cause of ocean acidification?
The primary cause of ocean acidification is the absorption of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere into the oceans.
How does ocean acidification impact marine organisms?
Ocean acidification can impair the ability of marine organisms to build and maintain their shells and skeletons, leading to reduced growth, survival, and reproductive success.
What are potential solutions to mitigate ocean acidification?
Potential solutions include reducing carbon emissions, enhancing carbon sequestration, and developing technologies to remove CO2 from the atmosphere.