Ventilator low pressure alarm causes are a common challenge in mechanical ventilation. These alarms can indicate a variety of underlying issues, from circuit leaks to patient factors, and can have a significant impact on patient outcomes. Understanding the causes of these alarms and implementing effective troubleshooting strategies is essential for ensuring optimal patient care.
Low pressure alarms are triggered when the ventilator detects a drop in airway pressure below a preset threshold. This can be caused by a number of factors, including:
Ventilator Low Pressure Alarm Causes
Ventilator low pressure alarms are triggered when the pressure in the ventilator circuit falls below a preset threshold. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Circuit leaks
- Patient factors
- Ventilator settings
Circuit Leaks
Circuit leaks are the most common cause of ventilator low pressure alarms. They can occur anywhere in the circuit, from the patient’s airway to the ventilator itself. Common sources of leaks include:
- Loose connections
- Cracked or damaged tubing
- Uncuffed endotracheal tubes
Patient Factors
Patient factors that can contribute to ventilator low pressure alarms include:
- Increased airway resistance
- Bronchospasm
- Mucus plugging
Ventilator Settings
Ventilator settings that can lead to low pressure alarms include:
- Low peak inspiratory pressure
- High positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP)
- Rapid respiratory rate
Troubleshooting Low Pressure Alarms
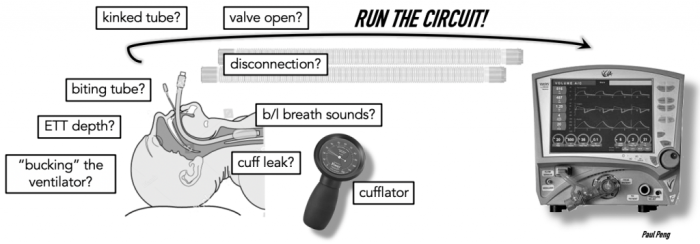
Troubleshooting low pressure alarms involves identifying and addressing the underlying cause. The following steps can be used:
- Check the circuit for leaks.
- Assess patient factors.
- Optimize ventilator settings.
Checking the Circuit for Leaks
To check the circuit for leaks, listen for audible leaks and inspect the circuit for any visible leaks. Common areas to check include:
- Connections between the patient and the ventilator
- Tubing
- Endotracheal tube cuff
Assessing Patient Factors
Patient factors that can contribute to low pressure alarms should be assessed. This includes:
- Airway resistance
- Bronchospasm
- Mucus plugging
Optimizing Ventilator Settings
Ventilator settings should be optimized to prevent low pressure alarms. This includes:
- Setting an appropriate peak inspiratory pressure
- Setting an appropriate PEEP
- Setting an appropriate respiratory rate
Impact of Low Pressure Alarms on Patient Outcomes: Ventilator Low Pressure Alarm Causes
Ventilator low pressure alarms can have a significant impact on patient outcomes. Hypoventilation, oxygen desaturation, and increased risk of complications can occur if the alarm is not promptly addressed.
Hypoventilation, Ventilator low pressure alarm causes
Hypoventilation occurs when the ventilator is not delivering enough air to the patient. This can lead to a decrease in the patient’s blood oxygen levels and an increase in the patient’s carbon dioxide levels.
Oxygen Desaturation
Oxygen desaturation occurs when the patient’s blood oxygen levels fall below normal. This can lead to tissue damage and organ failure.
Increased Risk of Complications
Low pressure alarms can also increase the risk of complications, such as:
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia
- Atelectasis
- Death
Strategies for Preventing Low Pressure Alarms

| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Optimize ventilator settings | Set appropriate peak inspiratory pressure, PEEP, and respiratory rate. |
| Ensure proper circuit connections | Check all connections between the patient and the ventilator for leaks. |
| Address patient factors | Assess for airway resistance, bronchospasm, and mucus plugging. |
| Use a high-pressure alarm | Set a high-pressure alarm to alert you to potential leaks or other problems. |
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
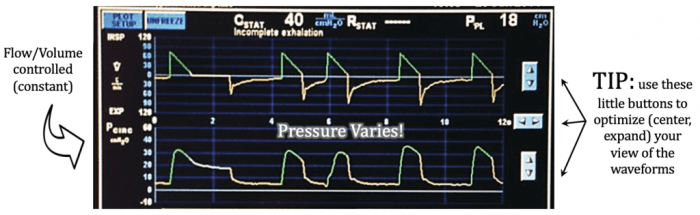
- Use a manometer to measure airway pressure.
- Evaluate the ventilator waveform.
- Consider potential equipment malfunctions.
Role of Respiratory Therapists in Managing Low Pressure Alarms
Respiratory therapists play a vital role in managing ventilator low pressure alarms. They are responsible for:
- Identifying low pressure alarms
- Troubleshooting the cause of the alarm Resolving the alarm
- Educating patients and families about low pressure alarms
Clarifying Questions
What are the most common causes of ventilator low pressure alarms?
The most common causes of ventilator low pressure alarms include circuit leaks, patient factors such as increased airway resistance or secretions, and ventilator settings that are not optimized for the patient’s needs.
How can I troubleshoot a ventilator low pressure alarm?
To troubleshoot a ventilator low pressure alarm, check the circuit for leaks, assess the patient for factors that may be contributing to the alarm, and optimize the ventilator settings. If the alarm persists, consider advanced troubleshooting techniques such as using a manometer to measure airway pressure or evaluating the ventilator waveform.
What is the impact of ventilator low pressure alarms on patient outcomes?
Ventilator low pressure alarms can have a significant impact on patient outcomes. Hypoventilation, oxygen desaturation, and increased risk of complications can occur if the underlying cause of the alarm is not promptly addressed.