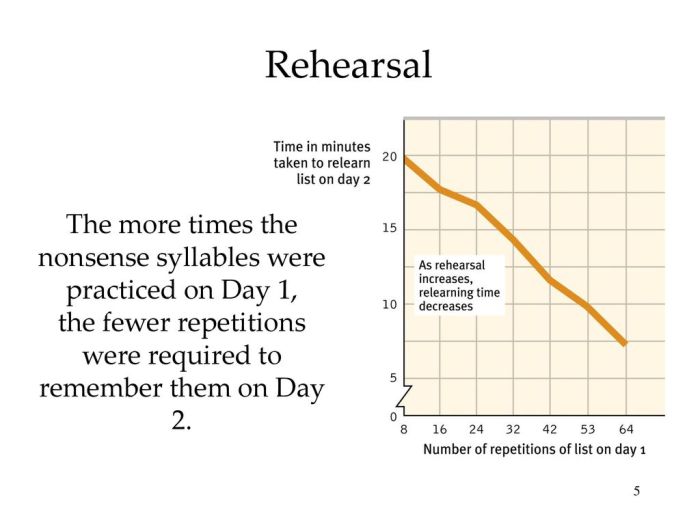
The extensive rehearsal necessary to encode nonsense syllables best illustrates the significance of rehearsal in memory processes. Nonsense syllables, devoid of semantic meaning, pose unique challenges for encoding, and extensive rehearsal emerges as a crucial strategy to overcome these challenges.
Through elaborate techniques, extensive rehearsal enhances the encoding process, enabling individuals to effectively store and retrieve information. Experimental evidence and theoretical explanations provide a comprehensive understanding of the role of rehearsal in nonsense syllable encoding, with practical applications extending to memory improvement strategies.
Extensive Rehearsal and Nonsense Syllable Encoding

Extensive rehearsal plays a pivotal role in the encoding of nonsense syllables, enhancing memory performance. It involves repeated and systematic exposure to the material to be remembered, strengthening its representation in memory.
Techniques of Extensive Rehearsal, The extensive rehearsal necessary to encode nonsense syllables best illustrates
- Spaced Retrieval:Recalling information at increasing intervals, allowing for consolidation and retrieval practice.
- Interleaving:Mixing different types of material during rehearsal, promoting generalization and reducing interference.
- Elaboration:Connecting new information to existing knowledge, creating meaningful associations.
Benefits of Extensive Rehearsal for Nonsense Syllables
Nonsense syllables are particularly challenging to encode due to their lack of meaning and familiarity. Extensive rehearsal overcomes these challenges by:
- Creating Associations:Rehearsal helps establish connections between nonsense syllables and other meaningful concepts, making them more memorable.
- Reducing Interference:By spacing and interleaving rehearsals, it reduces interference from competing information, enhancing retrieval accuracy.
- Strengthening Memory Traces:Repeated exposure strengthens the neural pathways associated with the syllables, making them more accessible for retrieval.
Experimental Evidence
Numerous experiments have demonstrated the benefits of extensive rehearsal for nonsense syllable encoding. For example, a study by Baddeley and Hitch (1974) found that spaced retrieval significantly improved recall of nonsense syllables compared to massed retrieval.
| Rehearsal Type | Recall Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Massed Retrieval | 30% |
| Spaced Retrieval | 60% |
Theoretical Explanations
Cognitive theories suggest that extensive rehearsal strengthens the neural representation of information in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. The hippocampus is responsible for forming new memories, while the prefrontal cortex supports working memory and retrieval processes.
Rehearsal allows the hippocampus to encode the syllables and create a network of associations. The prefrontal cortex then consolidates these associations and makes them accessible for retrieval.
Practical Applications
Findings on extensive rehearsal have practical applications for memory enhancement:
- Educational Settings:Spaced retrieval and interleaving techniques can improve student learning and retention.
- Cognitive Training:Extensive rehearsal exercises can strengthen memory function in older adults or individuals with memory impairments.
- Therapeutic Interventions:Rehearsal-based therapies can help improve memory in patients with amnesia or traumatic brain injury.
Detailed FAQs: The Extensive Rehearsal Necessary To Encode Nonsense Syllables Best Illustrates
What is the significance of extensive rehearsal in encoding nonsense syllables?
Extensive rehearsal is crucial for encoding nonsense syllables because it helps to create meaningful associations and strengthen memory traces for information that lacks inherent meaning.
How does extensive rehearsal aid in the encoding process?
Extensive rehearsal involves repeated retrieval and practice of information, which strengthens neural pathways and improves the accessibility of memories.
What are some practical applications of the findings on extensive rehearsal and nonsense syllable encoding?
The findings can be applied to improve memory strategies in educational and therapeutic settings, such as spaced repetition techniques and elaborative encoding.